Inflammatory Response
by Michael Shih
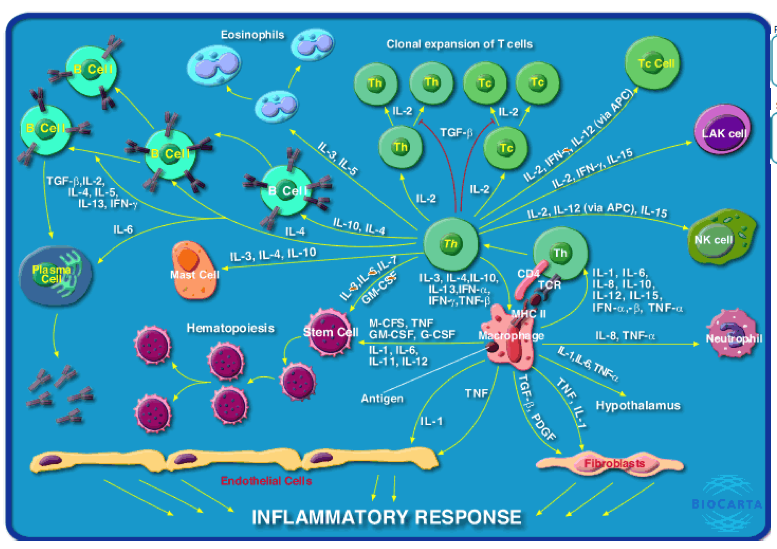
Figure constructed using Janis Kuby, Immunology (3rd ed.), Figure 13-4
Inflammation is a protective response to infection by the immune system that requires communication between different classes of immune cells to coordinate their actions.
- Acute inflammation is an important part of the immune response, but
- chronic inappropriate inflammation can lead to destruction of tissues in
- autoimmune disorders and
- perhaps neurodegenerative or cardiovascular disease.
Secreted cytokine proteins provide signals between immune cells to coordinate the inflammatory response.
- Some cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6 (see IL-6 pathway) and TNF (see TNFR1 and TNFR2 pathways) act to broadly provoke the inflammatory response while
- others act on specific types of immune cells.
Macrophages and other phagocytotic cells provide a front-line defense against bacterial infection.
Macrophages stimulate the inflammatory responses of
- neutrophils,
- fibroblasts, and
- endothelial cells
in response infection by secreting IL-1 and TNF.
- IL-1 and TNF cause fever through alteration of the body temperature set-point in the hypothalamus.
- Fibroblasts and endothelial cells respond to IL-1 and TNF by recruiting more immune cells to the site of inflammation.
- Secreted IL-8 is a chemokine that attracts neutrophils to sites of infection.
Macrophages also present antigen to T helper cells that play a central role in coordinating immune responses.
- T helper cells induce clonal expansion of T cells that respond to antigen, with IL-2 as a key mediator of T cell proliferation and activation (see IL-2 pathway).
- TGF-beta is a negative regulator of proliferation in many cells, have anti-inflammatory actions in some settings (see TGF-beta pathway).
- The cytotoxic activity of Natural Killer cells (NK cells) and lymphokine activated killer cells (LAK cells) toward viral infected or tumor cells is stimulated by IL-2 and other cytokines.
- T helpers secrete IL-3 and IL-5 to stimulate eosinophil proliferation and activation (see IL-5 pathway).
- Eosinophils are involved in the immune response to parasitic infection.
- T helper cells are required to stimulate B cell responses as well, with the cytokines IL-10, IL-4 and other cytokines regulating
- the clonal selection and
- differentiation of antigen-specific B cells to form antibody-secreting plasma B cells and memory cells.
In addition to inducing activation and proliferation of specific differentiated immune cells, cytokines act on hematopoeitic stem cells, causing their proliferation and differentiation into the full range of immune cells.
For pahtways click BioCharta Pathways or here (MacOS WebArchive)
Version: 22 February 2016
Address of this Page
Home
Joachim Gruber

